Guided surgery in dental implants is a modern, precision-based approach using advanced technology to plan and execute implant placement accurately, enhancing predictability and minimizing complications․
Definition and Overview
Guided surgery in dental implants involves using advanced digital technology to precisely plan and execute implant placement․ It relies on detailed 3D imaging and surgical guides to ensure accuracy, minimizing complications and enhancing outcomes․ This method allows for customized treatment plans, improving predictability and patient comfort․ By combining digital tools with clinical expertise, guided surgery streamlines the process, making it more efficient and less invasive compared to traditional techniques․
Types of Guided Surgery
Guided surgery for dental implants can be categorized into static and dynamic techniques․ Static guided surgery uses pre-fabricated surgical guides based on 3D imaging, while dynamic techniques employ real-time navigation systems․ Additionally, fully guided and partially guided methods are available, offering varying levels of precision; Each type is tailored to specific patient needs, ensuring optimal results․ These variations allow clinicians to choose the most suitable approach, balancing accuracy, complexity, and patient-specific factors for successful implant placement․
Advantages of Guided Surgery
Guided surgery offers enhanced precision, reducing the risk of complications and improving implant placement accuracy․ It minimizes trauma to surrounding tissues, promoting faster healing and patient comfort․ The use of pre-operative 3D planning ensures optimal positioning, maximizing aesthetic and functional outcomes․ Additionally, guided techniques often reduce surgery time and the need for bone grafting․ This approach enhances patient satisfaction and streamlines the treatment process, making it a preferred choice for both clinicians and patients seeking predictable and successful implant outcomes․
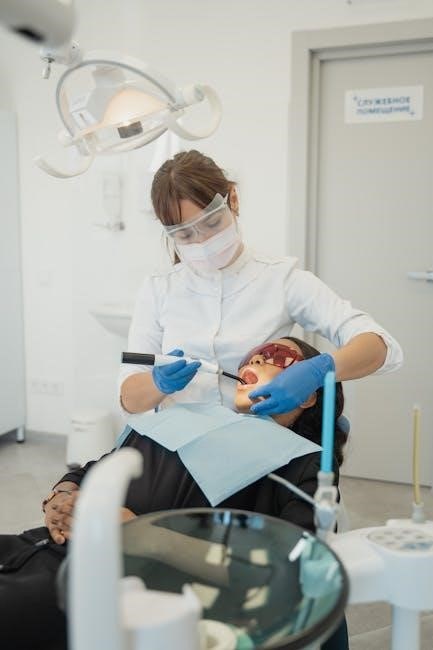
The Procedure of Guided Surgery Dental Implant
Guided surgery involves precise digital planning using 3D models to create a surgical guide, ensuring accurate implant placement and minimizing complications for faster recovery and optimal results․
Pre-Surgery Planning and Preparation
Pre-surgery planning involves detailed assessments using 3D imaging and CBCT scans to evaluate jaw structure, bone density, and nerve locations․ A customized surgical guide is created, ensuring precise implant placement․ Advanced software like RealGUIDE aids in virtual planning, simulating outcomes and minimizing complications․ Patient-specific factors, such as anatomical constraints and aesthetic preferences, are considered․ This meticulous preparation enhances accuracy, reduces surgery time, and improves overall success rates, ensuring a personalized and predictable outcome for each patient․
Step-by-Step Surgical Process
The procedure begins with administering local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort․ A surgical guide, created from pre-surgery planning, is placed in the mouth to direct precise implant placement․ The dentist drills pilot holes through the guide, following the planned trajectory․ The implant is then carefully inserted into the jawbone․ After placement, the site is closed with sutures or a healing cap․ In some cases, a temporary crown is attached immediately․ The process is minimally invasive, reducing recovery time and ensuring accuracy, guided by advanced tools like RealGUIDE software for optimal results․
Use of Anesthesia and Patient Comfort
Local anesthesia is typically administered to numb the surgical area, ensuring minimal discomfort during the procedure․ Sedation options, such as conscious sedation, may also be offered to anxious patients․ The use of advanced surgical guides allows for precise implant placement, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues and minimizing pain․ Patients often report feeling numb but comfortable during the surgery․ Post-operative discomfort is usually mild and managed with over-the-counter pain relievers․ The focus on patient comfort enhances the overall experience, making guided surgery a stress-free and efficient procedure․

Key Considerations in Guided Surgery
Guided surgery emphasizes precision, minimizing complications and ensuring optimal implant placement․ Patient anatomy, bone density, and restorative needs are carefully evaluated for tailored outcomes․
Success Rates and Clinical Outcomes
Guided surgery dental implants demonstrate high success rates, with studies showing over 95% survival rates in clinical outcomes․ The precision achieved through advanced planning reduces complications and enhances osseointegration․ Patients benefit from faster healing and improved functional results․ Research highlights that guided surgery minimizes errors compared to freehand techniques, leading to better long-term stability and aesthetic outcomes․ Proper planning and technology play a crucial role in achieving these favorable results, making guided surgery a reliable choice for dental implant procedures․
Potential Risks and Complications
While guided surgery dental implants are highly precise, potential risks include sinus perforation, nerve damage, or implant failure․ Sinus complications may arise if implants are placed too close to sinus cavities․ In rare cases, improper placement or infection can lead to failure․ Patient-specific anatomical challenges and surgical technique play a role in these complications․ Proper pre-surgery planning and experienced surgeons minimize these risks, but patients should be aware of possible issues․ Regular follow-ups and adherence to post-surgery care are crucial to mitigate these complications and ensure long-term success․
Guided vs․ Freehand Surgery: A Comparison
Guided surgery utilizes advanced technology, such as 3D imaging and precision guides, to plan and execute implant placement with high accuracy, minimizing complications and enhancing predictability․ In contrast, freehand surgery relies on the surgeon’s skill and experience without technological aids, offering adaptability but potentially higher risks․ Guided methods often involve detailed pre-operative planning to avoid critical structures, leading to more predictable outcomes; Freehand surgery, while effective, may lack the same level of precision․ Patient-specific factors, such as bone density, influence the choice of method․ Guided surgery may be preferable for complex cases, while freehand surgery suits straightforward scenarios․ Recovery times and costs also differ, with guided surgery potentially offering faster healing due to reduced tissue trauma, though at a higher expense․ Success rates and surgeon expertise play significant roles, with guided techniques possibly becoming the modern standard․ Understanding these differences aids in selecting the optimal approach for individual patient needs․

Cultural, Psychological, and Religious Influences
Cultural and religious beliefs significantly influence treatment choices, while psychological factors impact patient decisions and satisfaction in guided surgery dental implant procedures․
Cultural and Religious Factors in Treatment Choices
Cultural and religious beliefs significantly influence patient decisions in guided surgery dental implant treatments․ Practices such as avoiding certain materials or preferring specific graft sources are common․ For example, some cultures may favor autografts over allografts due to religious reasons․ These preferences often stem from ethical, moral, or traditional values․ Dental professionals must accommodate these beliefs to ensure patient comfort and satisfaction․ By doing so, they foster trust and adherence to treatment plans, leading to better overall outcomes and higher patient satisfaction rates․
Psychological Impact on Patient Decision-Making
Psychological factors play a crucial role in patient decision-making for guided surgery dental implants․ Anxiety, fear of pain, and concerns about the procedure’s success often influence choices․ Some patients may hesitate due to past negative dental experiences, while others may feel reassured by the precision and predictability of guided surgery․ The desire for improved aesthetics and function can also motivate patients․ Addressing these psychological aspects through clear communication and personalized care enhances patient confidence and satisfaction, ultimately shaping their treatment decisions and outcomes․
Patient Preferences and Satisfaction
Patient preferences often lean toward minimally invasive and precise procedures, making guided surgery a favored choice․ Many patients appreciate the reduced recovery time and high success rates associated with this method․ Satisfaction levels are heightened due to the use of advanced technology, which enhances accuracy and minimizes complications․ Additionally, the ability to visualize results pre-operatively aligns with patient expectations for aesthetics and functionality․ Personalized treatment plans further contribute to higher patient satisfaction, ensuring their specific needs and preferences are met throughout the dental implant journey;
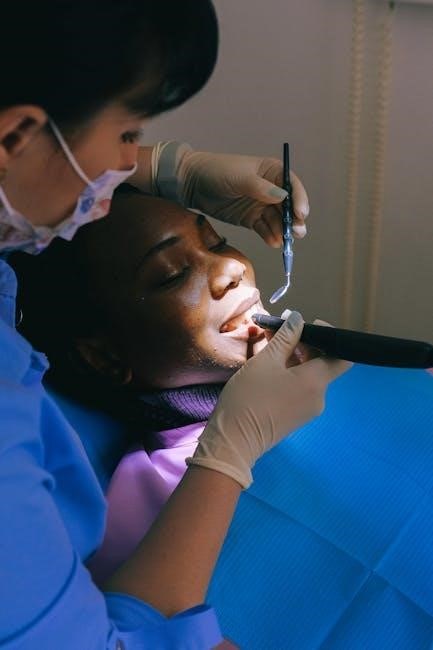
Recovery and Healing Process
The recovery process involves gradual healing of the implant site, with proper oral hygiene and dietary adjustments aiding faster osseointegration and minimizing complications․
Post-Surgery Recovery Timeline
The recovery process after guided surgery typically begins with mild swelling and discomfort, subsiding within a few days․ Patients can resume normal activities shortly, with dietary restrictions easing gradually․ The healing of soft tissues occurs within 1-2 weeks, while osseointegration, where the implant fuses with the jawbone, takes 3-6 months․ Proper oral hygiene and follow-up appointments ensure optimal healing, minimizing complications and supporting long-term implant success․
Factors Affecting Healing and Osseointegration
Healing and osseointegration success depend on factors like bone quality, implant fit, and patient health․ Smoking and diabetes can slow healing, while proper surgical technique and guided precision enhance integration․ Post-surgical care, including diet and hygiene, plays a crucial role․ The use of advanced materials and technologies also influences the fusion of the implant with the jawbone, ensuring stability and long-term functionality․
Tips for Faster Recovery
To promote faster recovery after guided dental implant surgery, adhere to post-operative instructions, maintain good oral hygiene, and avoid smoking․ Stick to a soft-food diet initially and stay hydrated․ Manage pain with prescribed medications and attend follow-up appointments․ Avoid strenuous activities and ensure proper wound care․ These steps enhance healing, reduce complications, and support osseointegration for optimal results and a smoother recovery process․
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Address common concerns about guided dental implant surgery, such as recovery time, risks, and success rates, to help patients make informed decisions about their treatment․
Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Many patients worry about pain during guided dental implant surgery, but most report minimal discomfort due to local anesthesia․ Another misconception is that it’s a lengthy process, when in fact, guided surgery often reduces procedure time․ Some fear high costs, but long-term benefits justify the investment․ Additionally, concerns about failure rates are addressed by high success rates and precise planning․ Understanding these aspects helps dispel myths and ensures informed decisions․
Addressing Patient Queries
Dentists often address patient queries by explaining the benefits of guided surgery, such as reduced recovery time and higher accuracy․ Patients frequently ask about the success rate, which is typically high due to precise planning․ They also inquire about the cost and whether insurance covers it․ Additionally, concerns about the procedure’s length and discomfort are common, but most find it manageable with anesthesia․ Open communication helps patients feel informed and confident about their decision to proceed with guided dental implant surgery․
Long-Term Maintenance and Care
Long-term maintenance for guided surgery dental implants involves regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and avoiding habits like smoking or excessive alcohol․ Patients are advised to follow specific care instructions to ensure the longevity of their implants․ Proper cleaning and monitoring by a dentist are crucial to prevent complications․ With consistent care, implants can last for decades, providing a durable and natural-looking solution for missing teeth․ Regular maintenance ensures the implants remain functional and aesthetically pleasing over time․

Modern Tools and Software in Guided Surgery
Modern tools like RealGUIDE software and Guide Mia enhance precision in guided surgery, offering 3D planning and real-time navigation for accurate dental implant placement and improved outcomes․
RealGUIDE Software and Its Benefits
RealGUIDE software is a cutting-edge tool for guided surgery, offering 3D planning and real-time navigation for dental implant placement․ Its user-friendly interface simplifies complex procedures, enhancing accuracy and reducing complications․ With features like virtual implant placement and precise drilling guides, it ensures optimal results․ RealGUIDE also provides a free trial, making it accessible for clinicians to adopt․ By streamlining the surgical process, it improves patient outcomes and satisfaction, making it a valuable asset in modern implantology․
Other Advanced Surgical Guide Systems
Beyond RealGUIDE, other advanced systems like NobelGuide and All-on-4 offer precise implant placement through detailed 3D planning․ These tools enable clinicians to visualize optimal implant positions, improving accuracy and reducing surgical time․ With features like customizable templates and real-time feedback, they enhance patient-specific outcomes․ Such systems also integrate seamlessly with modern imaging technologies, ensuring minimally invasive procedures․ Their adoption has significantly elevated the standards of guided surgery, offering reliable solutions for complex cases and improving overall patient satisfaction in dental implantology․
Guide Mia: Features and Capabilities
Guide Mia is a powerful tool in guided surgery, offering advanced features for precise implant placement․ Its capabilities include 3D planning, real-time navigation, and compatibility with various implant systems․ The software provides detailed visualization, enhancing surgical accuracy and reducing complications․ While its interface may appear outdated, Guide Mia’s functionality is robust, allowing for complex case management with ease․ It stands out for its versatility and ability to adapt to individual patient needs, making it a valuable asset in modern dental implant procedures․