The anatomy of sports injuries is crucial for understanding injury mechanisms, prevention, and recovery. This guide provides detailed insights into injury types, recovery strategies, and rehabilitation techniques, helping athletes and fitness enthusiasts optimize their performance and health.
Overview of Sports Injuries
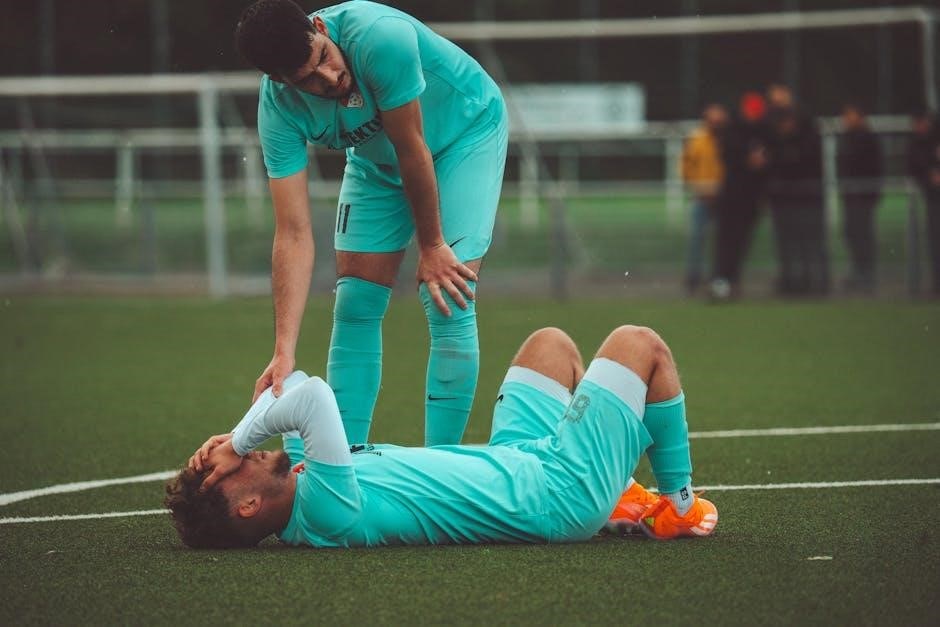
Sports injuries are a common challenge for athletes and fitness enthusiasts, impacting performance and overall well-being. Overuse injuries account for 30-50% of all sports injuries, often due to repetitive strain, while acute injuries result from sudden trauma. Understanding the anatomy of these injuries is key to prevention and recovery. Common injuries include muscle strains, tendinitis, and ligament sprains, each requiring specific approaches for healing. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, helping individuals identify injury types, understand their causes, and implement effective recovery strategies. By addressing both acute and chronic conditions, it equips readers with the knowledge to mitigate risks and maintain peak physical condition.
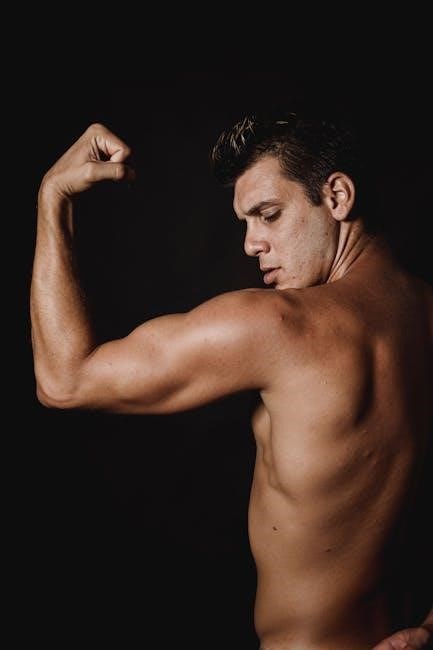

Understanding Sports Injuries
Understanding sports injuries involves identifying their causes, such as overuse, poor training techniques, or biomechanical imbalances. This knowledge aids in effective recovery and prevention strategies.
Types and Classifications of Injuries
Sports injuries are broadly categorized into acute and overuse types. Acute injuries occur suddenly, often due to trauma, such as fractures or ligament sprains. Overuse injuries develop gradually from repetitive stress, like tendonitis or stress fractures. Injuries are further classified by severity, ranging from mild (e.g., minor strains) to severe (e.g., complete ligament tears). They can also be grouped by body region, such as lower extremity injuries (e.g., hamstring strains) or upper extremity injuries (e.g., shoulder impingements). Understanding these classifications helps in tailoring rehabilitation programs and prevention strategies, addressing both the injury’s nature and its impact on specific anatomical structures.
Anatomy of Sports Injuries
Sports injuries often involve muscles, tendons, and joints. Understanding their anatomy helps identify injury causes and optimize recovery. Common injuries include strains, sprains, and overuse damage.
Regional Anatomy and Common Injury Sites
Understanding regional anatomy is key to identifying common injury sites. The lower extremities, such as knees and ankles, are prone to overuse injuries from repetitive stress. The upper body, particularly shoulders and elbows, often suffers from repetitive motion injuries in sports like tennis or baseball. Core and lower back injuries are common due to poor posture or improper lifting techniques. Each region has specific vulnerabilities, and recognizing these areas helps in preventing and rehabilitating injuries effectively. This knowledge is essential for fitness enthusiasts and athletes to maintain optimal performance and reduce the risk of long-term damage.
Prevention Strategies
Effective prevention strategies include strengthening exercises, proper warm-ups, and technique training; These methods enhance strength, flexibility, and coordination, reducing injury risks and promoting long-term fitness.
Strengthening Exercises and Warm-Up Routines
Strengthening exercises and warm-up routines are essential for injury prevention and enhanced performance. Targeted exercises improve muscle strength, joint stability, and flexibility, reducing the risk of overuse and acute injuries. Dynamic warm-ups, such as leg swings and arm circles, prepare the body for physical activity by increasing blood flow and muscle temperature. Incorporating resistance training and functional movements helps athletes build resilience in injury-prone areas. Properly designed routines also enhance proprioception and coordination, ensuring optimal movement patterns. By prioritizing these practices, individuals can create a foundation for safer, more effective workouts and sports participation, aligning with the principles outlined in resources like The Anatomy of Sports Injuries.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Clinical evaluation and diagnostic imaging are critical for accurately identifying sports injuries; Proper assessment ensures targeted rehabilitation, reducing recovery time and preventing further damage to affected areas.
Clinical Evaluation and Diagnostic Imaging
A comprehensive clinical evaluation is the cornerstone of diagnosing sports injuries, combining patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. This process ensures accurate identification of injury severity and type. Diagnostic tools like X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasounds provide detailed visuals of damaged tissues, aiding in precise diagnoses. A thorough assessment helps differentiate between acute and chronic injuries, guiding tailored rehabilitation plans. Accurate imaging also identifies underlying anatomical issues, such as fractures or ligament tears. By integrating clinical findings with imaging results, healthcare professionals can develop effective treatment strategies, ensuring optimal recovery and minimizing recurrence risks for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.

Rehabilitation Techniques
Rehabilitation techniques focus on restoring function, strength, and mobility through targeted exercises, therapeutic modalities, and progressive loading, ensuring a safe return to activity.
Exercise Programs and Rehabilitation Modalities
Effective rehabilitation combines structured exercise programs with therapeutic modalities to enhance recovery. Strengthening exercises, flexibility routines, and proprioceptive training are cornerstone techniques. Modalities like ice therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation reduce inflammation and pain. Progressive overload ensures tissues adapt without re-injury. Hydrotherapy and balance exercises improve joint stability and mobility. Personalized programs address specific injury sites, fostering optimal healing. These methods, detailed in resources like The Anatomy of Sports Injuries, empower athletes to regain function and return to activity safely. By integrating exercises with advanced modalities, rehabilitation promotes long-term resilience and performance.
Psychological Aspects
Sports injuries profoundly impact mental health, causing anxiety, fear of re-injury, and changes in body image. A positive mindset and mental recovery strategies are crucial for overcoming these challenges.
Mental Recovery and Athlete Mindset
Sports injuries often lead to psychological challenges, including Real-world examples illustrate injury recovery processes, offering insights into athletes’ journeys and rehabilitation strategies. These studies highlight specific injuries, treatments, and outcomes, fostering evidence-based recovery practices. Case studies highlight real-world injury recovery scenarios, showcasing athletes’ journeys from diagnosis to full rehabilitation. For instance, elite athletes with tendon overuse injuries demonstrate how targeted exercises and modalities accelerate healing. Gymnasts with chronic stress fractures illustrate the importance of nutritional interventions and progressive loading. A footballer’s recovery from an ACL tear underscores the role of surgical reconstruction and neuromuscular training. These examples provide practical insights into injury-specific rehabilitation, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment plans and multidisciplinary care. Such case studies empower athletes and practitioners with evidence-based strategies for optimal recovery and performance restoration. Proper nutrition is vital for injury healing; Key strategies include consuming protein for tissue repair, omega-3s to reduce inflammation, and antioxidants to combat muscle damage. Adequate hydration and carbohydrates support energy replenishment and recovery. Proper nutrition plays a critical role in injury recovery. A diet rich in protein helps repair damaged tissues, while omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation. Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, combat oxidative stress. Hydration is essential for tissue repair and joint health. Carbohydrates provide energy for recovery, and fiber supports gut health. Timing meals around workouts and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric and ginger can enhance healing. Avoiding processed foods and focusing on whole, nutrient-dense meals ensures optimal recovery. Supplements like collagen or glutamine may also aid tissue repair. A balanced diet tailored to injury needs accelerates recovery and supports long-term health. Long-term management focuses on chronic injury care, lifestyle adjustments, and personalized exercise plans to maintain functionality and prevent recurrence, ensuring sustainable health and mobility for athletes. Chronic injury care requires a comprehensive approach, integrating medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and adaptive exercises. Patients often need to adopt long-term rehabilitation strategies to manage pain and maintain functionality. Lifestyle adjustments may include ergonomic changes, dietary modifications, and stress management to support healing and prevent further damage. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals ensures personalized care plans are effective and sustainable. Additionally, patient education plays a vital role in empowering individuals to take an active role in their recovery, promoting independence and overall well-being. This holistic method addresses both physical and psychological aspects, fostering resilience and improving quality of life. Emerging technologies, such as AI-driven diagnostics and wearable devices, are revolutionizing sports injury rehabilitation. These innovations enable personalized recovery plans, enhancing efficiency and outcomes for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR) are transforming injury rehabilitation. AI-driven tools analyze injury patterns, creating personalized recovery plans, while VR provides immersive simulations for rehabilitation exercises. Wearable devices now track movement and biomechanics in real-time, reducing reinjury risks. Additionally, regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies are paving the way for faster tissue repair. These innovations, combined with data analytics, enable more precise and efficient rehabilitation programs, helping athletes return to peak performance sooner. The integration of these technologies marks a significant shift toward smarter, more effective injury management in sports and fitness. Understanding the anatomy of sports injuries is essential for effective prevention, diagnosis, and rehabilitation. By addressing the root causes of injuries and utilizing targeted exercises, athletes can accelerate recovery and reduce the risk of future harm. Emerging technologies, such as wearable devices and AI-driven tools, further enhance rehabilitation outcomes. A comprehensive approach combining anatomical knowledge, personalized strategies, and innovative techniques empowers individuals to achieve optimal performance and long-term health. Whether for fitness enthusiasts or elite athletes, prioritizing injury prevention and recovery ensures a safer, more sustainable path to achieving their goals and maintaining peak physical condition.
Case Studies
Real-World Examples of Injury Recovery
Nutrition and Recovery
Nutritional Strategies for Healing

Long-term Management
Chronic Injury Care and Lifestyle Adjustments

Future Trends
Emerging Technologies in Injury Rehabilitation